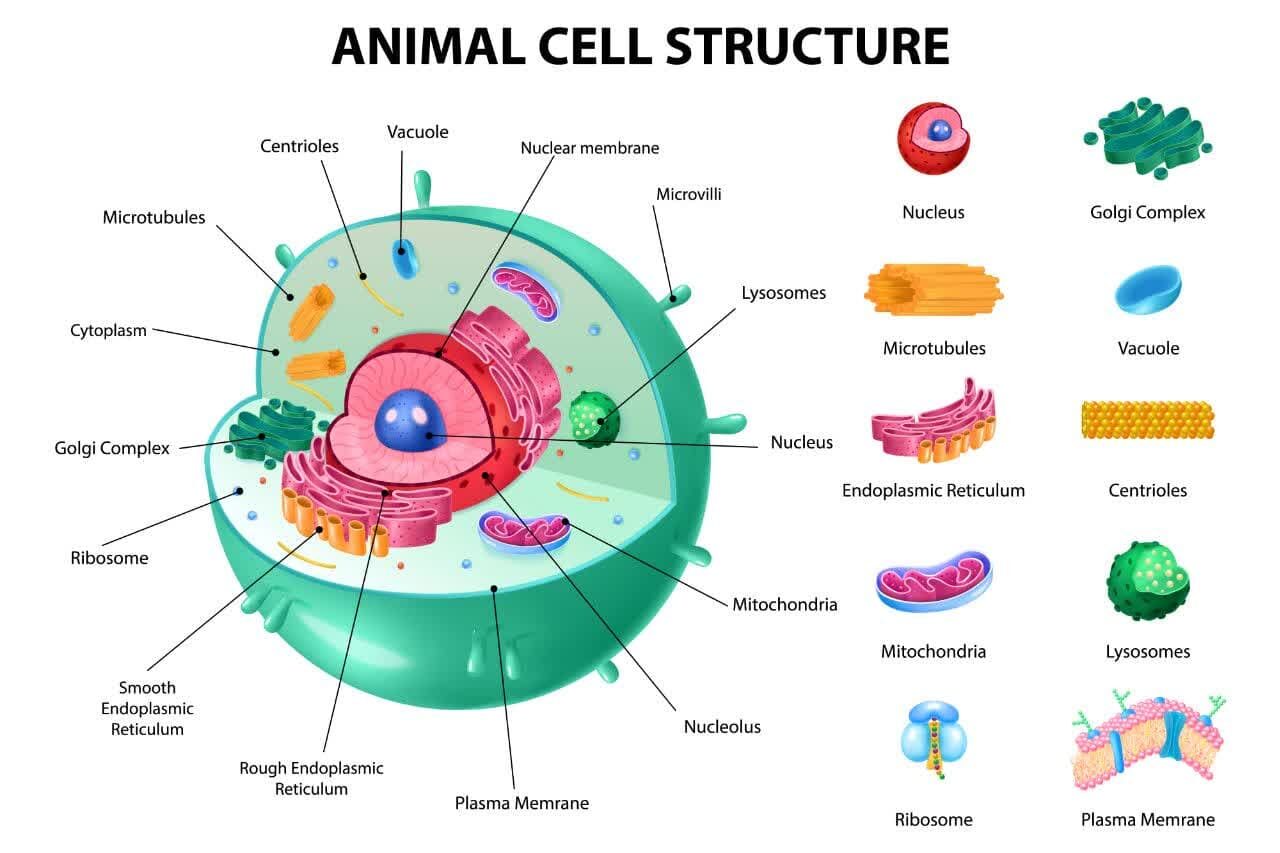
In the vast realm of biology, the animal cell stands as a remarkable marvel of nature’s ingenuity. Comprising a myriad of intricate structures and functions, the animal cell serves as the fundamental building block of all living organisms in the animal kingdom. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the captivating world of animal cells, unraveling their diverse components and elucidating their pivotal roles in sustaining life.
History and Discovery
The exploration of the animal cell’s origins and characteristics has been a fascinating journey throughout the history of scientific discovery. The story begins with the pioneering work of Robert Hooke in the 17th century, who first observed and named the “cells” in cork tissue. However, it was not until the 19th century that advancements in microscopy allowed for a more detailed understanding of the animal cell.
In the early 1800s, scientists such as Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann proposed the cell theory, which stated that all living organisms are composed of cells. This groundbreaking theory laid the foundation for further investigations into the animal cell. As technology improved, scientists were able to delve deeper into the intricate structures and functions of these cells.
One of the most significant breakthroughs in the history of animal cell discovery came in the late 19th century with the invention of the electron microscope. This powerful tool allowed scientists to visualize the ultrastructure of cells in unprecedented detail. With the electron microscope, researchers were able to identify organelles within the animal cell, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum.
Overall, the history of the discovery of the animal cell is a testament to the relentless pursuit of knowledge and the advancements in scientific techniques. From the initial observations of Robert Hooke to the development of the cell theory and the invention of the electron microscope, each milestone has contributed to our current understanding of the complex and intricate world of animal cells.
Introduction to Animal Cells:
At the heart of every living creature lies the animal cell, a microscopic powerhouse brimming with activity. Enclosed within a semi-permeable membrane, the animal cell harbors a complex array of organelles, each contributing to the cell’s vitality and functionality. From the nucleus, the cell’s command center housing its genetic material, to the mitochondria, the powerhouse responsible for energy production, animal cells exhibit a remarkable degree of specialization and sophistication.
Structural Composition:
The structural composition of animal cells is characterized by a dynamic interplay of organelles, cytoplasm, and cytoskeleton. At the core of the cell lies the nucleus, which houses the cell’s DNA and serves as the control center for cellular activities. Surrounding the nucleus, a network of endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and vesicles orchestrates the synthesis, modification, and transport of proteins and other molecules. Meanwhile, mitochondria generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s primary energy currency, through oxidative phosphorylation, fueling cellular processes and sustaining life.
Functional Significance:
The functionality of animal cells extends far beyond their structural organization, encompassing a diverse array of physiological processes essential for life. From cellular respiration to cellular division, animal cells exhibit remarkable versatility and adaptability to varying environmental conditions. Mitochondria play a central role in energy metabolism, converting nutrients into usable energy through aerobic respiration. Additionally, the endoplasmic reticulum facilitates protein synthesis and lipid metabolism, while the Golgi apparatus processes and packages molecules for secretion or intracellular transport.
Damage and Recovery:
The damage and subsequent recovery of animal cells are dynamic processes governed by a multitude of factors. When exposed to various stressors such as physical trauma, chemical toxins, or microbial pathogens, animal cells may incur damage to their structural integrity and biochemical functionality. This damage can manifest in a range of forms, including membrane disruption, organelle dysfunction, and DNA fragmentation. In response to such insults, cells activate intricate signaling pathways and molecular mechanisms aimed at mitigating damage and restoring cellular homeostasis.
Cellular recovery mechanisms involve a coordinated effort to repair and regenerate damaged components, thereby restoring cellular function and viability. One crucial aspect of cellular recovery is the activation of DNA repair mechanisms, which aim to correct DNA damage and prevent mutations that could compromise cellular integrity or lead to malignant transformation. Additionally, cells may undergo autophagy, a process wherein damaged organelles and cellular components are targeted for degradation and recycling, promoting cellular renewal and survival. Furthermore, the activation of stress response pathways such as the heat shock response and unfolded protein response helps cells cope with proteotoxic stress and maintain protein homeostasis.
The damage and subsequent recovery of animal cells represent intricate processes orchestrated by a myriad of cellular pathways and molecular players. Understanding the mechanisms underlying cellular damage and recovery not only sheds light on fundamental aspects of cell biology but also holds significant implications for various fields, including medicine and biotechnology. By elucidating the intricacies of cellular resilience and adaptation, researchers aim to develop novel therapeutic strategies for combating disease, promoting tissue regeneration, and enhancing cellular health and longevity.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the animal cell stands as a testament to the intricacies of life, embodying the remarkable complexity and elegance of biological systems. From its structural organization to its functional significance, the animal cell exemplifies nature’s ingenuity and adaptability, driving the myriad processes essential for life. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of cellular biology, the profound insights gained from studying animal cells pave the way for groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in science and medicine.